Welcome to ‘Understanding canine dental care Dog Teeth: Why Do They Fall Out and What You Can Do About It.’ As dog owners, we cherish our furry companions and strive to provide them with the best care possible. However, one aspect of canine health that often goes unnoticed until it becomes a problem is their dental health.

canine dental care , Dog
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of dog teeth, exploring why they fall out, the implications of tooth loss for your canine friend, and most importantly, what proactive steps you can take to ensure their dental well-being. Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the secrets behind those precious canine smiles and learn how to keep them shining bright.
Understanding Normal Teeth Shedding in Dogs
As pet parents, it’s essential to comprehend the natural processes that govern our furry friends’ health, including their dental hygiene. Just like humans, dogs undergo a phase of tooth development and shedding as they mature from puppies into adults. This shedding process is a natural and necessary part of their growth, ensuring that their mouths remain healthy and functional throughout their lives.
During the first few months of a puppy’s life, they possess a set of temporary or deciduous teeth, commonly referred to as “milk teeth.” These primary teeth serve their purpose in the early stages of development but eventually give way to a set of permanent adult teeth. This transition typically begins around the age of three to four months and continues until the puppy reaches around six to eight months of age.
The shedding of puppy teeth and the eruption of adult teeth can sometimes cause mild discomfort for your canine companion. You may notice increased chewing behavior or slight bleeding around the gums during this time. However, these symptoms are generally temporary and should resolve as the process completes.
It’s crucial to monitor your dog’s dental development during this period to ensure everything progresses as expected. Occasionally, retained deciduous teeth or abnormal tooth growth patterns may require veterinary attention to prevent potential dental issues later in life.
Once your dog has reached adulthood, their dental maintenance shifts to regular oral care practices, including brushing, dental chews, and professional cleanings. Understanding the natural shedding process of your dog’s teeth is the first step in promoting their long-term oral health and ensuring that they maintain a happy and comfortable smile throughout their lives.
Exploring the Causes of Abnormal Teeth Loss in canine dental care Dogs
While the shedding of deciduous (baby) teeth and the replacement with adult teeth is a natural process in a dog’s life, abnormal teeth loss can signal underlying health issues that require attention. Understanding the potential causes of abnormal teeth loss is crucial for proactive dental care and overall well-being for our furry companions.
- Periodontal Disease: One of the leading causes of tooth loss in dogs is periodontal disease, a bacterial infection affecting the gums and surrounding structures. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to gum recession, bone loss, and ultimately, tooth loss.
- Trauma or Injury: Dogs are active animals prone to accidents and injuries. Trauma to the mouth, such as blunt force trauma or chewing on hard objects, can result in fractured or dislodged teeth. Severe trauma may necessitate immediate veterinary intervention.
- Malocclusion: Malocclusion refers to misalignment of the teeth, leading to abnormal wear, pressure, and potential tooth loss. Certain breeds are predisposed to malocclusion, which can cause overcrowding, overlapping teeth, or abnormalities in jaw structure.
- Systemic Diseases: Some systemic diseases, such as diabetes or kidney disease, can affect oral health and contribute to tooth loss. These conditions may compromise the immune system or alter saliva composition, increasing susceptibility to dental problems.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition, particularly deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D, can impair dental development and weaken tooth structure. Poor diet can also contribute to gum disease and decay.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic conditions or inherited traits can predispose dogs to dental abnormalities, including early tooth loss. Breed-specific issues such as retained deciduous teeth or abnormal dental development may increase the risk.
- Tumors or Oral Lesions: Oral tumors, cysts, or other lesions in the mouth can cause localized tissue damage, leading to tooth loss. Additionally, tumors may exert pressure on surrounding structures, causing displacement or resorption of teeth.
- Immune-Mediated Disorders: Disorders affecting the immune system can manifest in various ways, including oral manifestations such as gingivitis, stomatitis, or periodontal disease, ultimately contributing to tooth loss.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, particularly long-term use of certain antibiotics or immunosuppressive drugs, can affect oral health and increase the risk of dental problems or tooth loss as a side effect.

canine dental care , Dog
Addressing abnormal teeth loss in dogs requires a thorough veterinary examination to identify the underlying cause and implement appropriate treatment strategies. Early detection and intervention are crucial for preserving oral health and ensuring your canine companion enjoys a happy, pain-free smile for years to come.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Dental Issues in Dogs
As vigilant pet parents, it’s essential to be attuned to potential signs and symptoms of dental problems in our canine companions. Early detection allows for timely intervention, preventing discomfort and maintaining optimal oral health. Stay vigilant for these telltale signs and symptoms :
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): Persistent foul odor emanating from your dog’s mouth, often beyond typical “doggy breath,” can indicate underlying dental issues such as gum disease or infection.
- Changes in Eating Habits: Difficulty chewing, reluctance to eat hard food, dropping food from the mouth, or preferring softer foods may signal oral discomfort or pain associated with dental problems.
- Excessive Drooling: While some drooling is normal, an increase in drooling, particularly if it’s accompanied by other symptoms, could indicate oral pain or irritation.
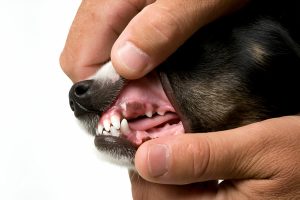
- Visible Tartar or Plaque Build-up: Yellow or brown deposits on the teeth, especially near the gumline, are signs of tartar accumulation, which can lead to gingivitis and periodontal disease if left untreated.
- Healthy gums: Typically, they’re pink and firm, but watch out for redness or inflammation.. Redness, swelling, or bleeding along the gumline may indicate gingivitis or periodontal disease.
- Loose or Missing Teeth: Teeth that are loose, broken, or missing altogether are obvious signs of dental problems and should prompt immediate veterinary attention.
- Changes in Behavior: If your dog displays signs of discomfort, such as pawing at the mouth, reluctance to be touched around the face, or increased irritability, it could indicate dental pain.
- Facial Swelling or Discharge: Swelling around the face or mouth, as well as discharge from the nostrils or eyes, may suggest an abscess or infection originating from dental issues.
- Changes in Vocalization: Whimpering, whining, or yelping while eating or when pressure is applied to the mouth may indicate oral pain.
- Reluctance to Play with Toys: Dogs with dental discomfort may avoid playing with toys that require chewing or may exhibit changes in their chewing habits.
- Weight Loss or Decreased Appetite: Chronic dental pain can lead to reduced food intake and subsequent weight loss if left untreated.
- Visible Signs of Oral Trauma: Any visible signs of trauma to the mouth, such as bleeding, lacerations, or foreign objects lodged between teeth, warrant immediate veterinary attention.
Regular dental check-ups with your veterinarian, along with proactive home dental care, are essential for maintaining your dog’s oral health. By staying alert to these signs and symptoms, you can ensure early intervention and help your canine companion enjoy a healthy and pain-free smile for years to come.
Preventive Care and Treatment Options for Canine Dental Health
Ensuring your dog’s dental health requires a combination of preventive care measures and prompt treatment when issues arise. Here’s a comprehensive guide to preventive care and treatment options:

canine dental care , Dog
Preventive Care:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule routine dental examinations with your veterinarian at least once a year, or as recommended based on your dog’s dental health status.
- Professional Dental Cleanings: Veterinary dental cleanings are essential for removing tartar and plaque buildup, which can lead to gum disease and tooth decay. These cleanings are performed under anesthesia to ensure thorough cleaning and minimize stress.
- Home Dental Care: Implement a daily dental hygiene routine at home, including brushing your dog’s teeth with a pet-safe toothpaste and toothbrush. Dental chews, dental diets, and water additives can also help reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
- Dietary Considerations: Feed your dog a balanced diet rich in nutrients, avoiding excessive sugary treats and hard, abrasive foods that can contribute to dental wear and tear.
- Chew Toys and Dental Treats: Offer dental-specific chew toys and treats designed to promote chewing and reduce plaque
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on your dog’s oral health and watch for any changes in behavior, eating habits, or signs of discomfort that may indicate dental problems.
Treatment Options:
- Professional Dental Cleanings: In addition to preventive cleanings, your veterinarian may recommend more frequent or specialized cleanings if your dog has existing dental issues or is at higher risk for dental disease.
- Extractions: If a tooth is severely damaged,
- Oral Surgery: Advanced dental procedures, such as root canal therapy or gum surgery, may be performed to save
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat oral infect
- Pain Management: Pain relief medications or anti-inflammatory drugs may be administered to manage discomfort associat
- Dietary Modifications: In some cases, dietary changes may be r
- Home Care Plans: Your veterinarian can provide guidance on ongoing hom
By prioritizing preventive care and seeking prompt veterinary attenti
Nurturing Your Dog’s Dental Health
As responsible pet parents, it’s our duty to prioritize the dental health of our beloved canine companions. In this guide, we’ve explored the intricate world of canine dental care, from understanding the natural processes of tooth shedding to identifying signs of dental issues and implementing preventive measures.
By staying vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your dog enjoys a lifetime of strong, healthy teeth and gums. Regular veterinary check-ups, coupled with a tailored dental care routine at home, form the foundation of preventive care. Brushing your dog’s teeth daily, offering dental chews and treats, and providing a balanced diet all contribute to maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
Moreover, recognizing the signs of dental problems and seeking timely veterinary intervention are crucial steps in preventing discomfort and addressing issues before they escalate. Whether it’s scheduling professional dental cleanings, treating oral infections, or providing pain management, your veterinarian plays a vital role in your dog’s dental care journey.
Remember, a healthy smile is not only a sign of your dog’s well-being but also enhances their overall quality of life. By investing in their dental health, you’re ensuring they can eat, play, and interact with comfort and confidence.
canine dental care , Dog
So, let’s commit to being proactive advocates for our furry friends’ dental wellness, because every wag of their tail and every joyful bark is worth protecting. Here’s to many more years of happy, healthy smiles with our canine companions!